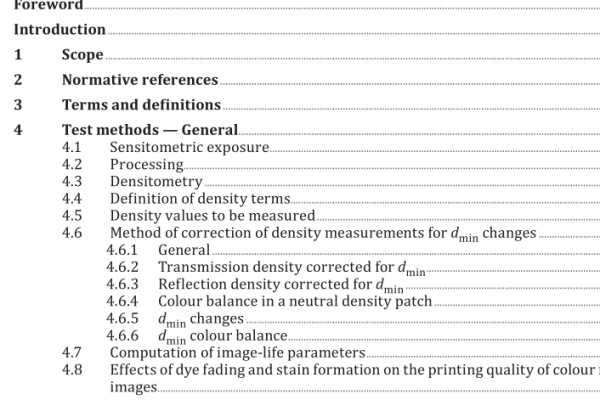
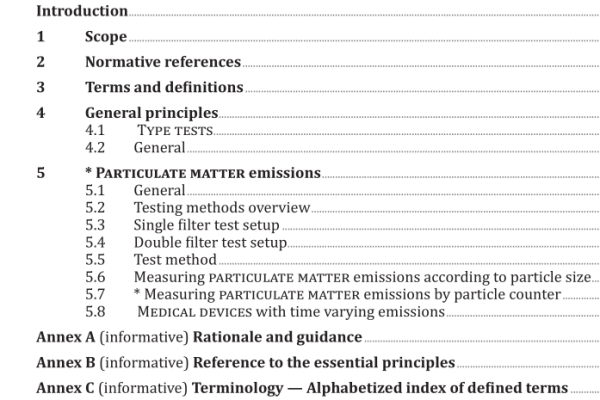
ISO IEC 20162:2001 pdf download – Information technology — Data interchange on 300 mm optical disk cartridges of type WORM (Write Once Read Many) using irreversible effects — Capacity: 30 Gbytes per cartridge.
4.3 Clamping Zone: The area of the disk within which the clamping force is applied by the clamping device.
4.4 Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC ): A method for detecting errors in data.
4.5 Data Zone: An annular area within the user zone on the disk having a constant data clock frequency.
4.6 defect management: A method for handling defective areas on the disk.
4.7 Disk Reference Plane: A plane defined by the perfectly flat annular surface of an ideal spindle onto which the Clamping Reference Area of the disk is clamped, and which is normal to the axis of rotation.
4.8 entrance surface: The surface of the disk on to which the optical beam first impinges.
4.9 Error Correction Code (ECC): An error-detecting code designed to correct certain kinds of errors in data.
4.10 format: The arrangement or layout of information on the disk.
4.11 hub: The central feature on the disk which interacts with the spindle of the disk drive to provide radial centring and the clamping force.
4.12 interleaving: The process of allocating the physical sequence of units of data so as to render the data more immune to burst errors.
4.13 Logical Sector: The minimum addressable user data block.
4.14 Logical Block Address: The address of a block of data.
4.15 mark: A feature of the recording layer, which may take the form of a pit, or any other type or form that can be sensed by the optical system. The pattern of marks represents the data on the disk.
4.16 mark edge: The transition between a region with a mark and one without a mark or vice versa, along the track.
4.17 mark edge recording: A recording method that uses a mark edge to represent a Channel bit.
4.18 optical disk: A disk that will accept and retain information in the form of marks in a recording layer that can be read with an optical beam.
4.19 optical disk cartridge (ODC): A device consisting of a case containing an optical disk.
4.20 polarization: The direction of polarization of an optical beam is the direction of the electric vector of the beam.
4.21 prerecorded mark: A mark written on the recording layer during manufacturing of the disk.
4.22 read power: The read power is the optical power, incident at the entrance surface of the disk, used when reading.
4.23 recording layer: A layer of the disk on, or in, which data is written during manufacture and/or use.
4.24 Reed-Solomon code: An error detection and/or correction code that is particularly suited to the correction of errors that occur in bursts or are strongly correlated.
4.25 space: The area between marks along the track.
4.26 spindle: The part of the disk drive which contacts the disk and/or hub.
4.27 substrate: A transparent layer of the disk, provided for mechanical support of the recording layer, through which the optical beam accesses the recording layer.
4.28 track: The path which is followed by the focus of the optical beam during one revolution of the disk.
4.29 track pitch: The distance between the centrelines of adjacent tracks, measured in a radial direction.
4.30 write-inhibit hole: A hole in the case which, when detected by the drive to be open, inhibits write operation.
ISO IEC 20162:2001 pdf download – Information technology — Data interchange on 300 mm optical disk cartridges of type WORM (Write Once Read Many) using irreversible effects — Capacity: 30 Gbytes per cartridge